人工智能赋能强迫症自助式智能心理干预新方案研究:
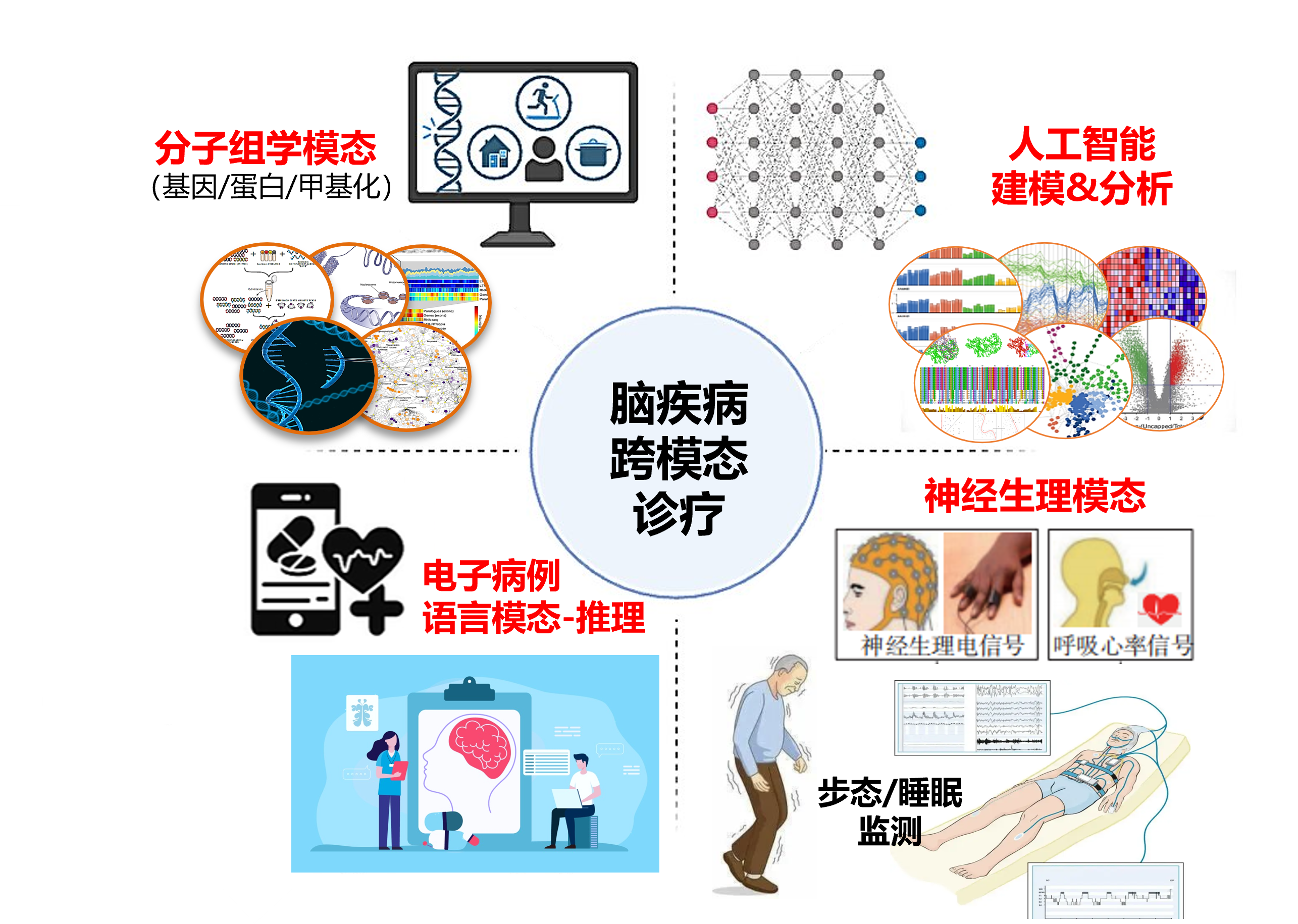
基于强迫症专病队列,通过磁共振、脑电图、神经心理血液等多维度数据,构建识别适用心理治疗个体的强迫症评估模型,建立以认知行为治疗与正念疗法为基础,融入个体化评估的强迫症自助式智能心理干预系统.
AI-Enabled Self-Guided Psychological Intervention for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder:
This study aims to develop a novel self-guided psychological intervention system for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) empowered by artificial intelligence. Leveraging a disorder-specific OCD cohort, we will integrate multi-dimensional data—including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), neuropsychological assessments, and peripheral blood biomarkers—to construct an individualized evaluation model for identifying patients most likely to benefit from psychological therapies. Based on this model, we will build a personalized, AI-assisted intervention platform grounded in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based approaches, enabling precision, scalability, and autonomy in OCD mental health care.

电子病历驱动的精神分裂症异质性智能解构与多模态诊疗决策模型研究:
本项目聚焦精神分裂症临床异质性难题,依托上海市精神卫生中心逾万例住院患者电子病历,构建电子病历驱动的智能诊疗决策模型。 融合多模态表征、自监督学习与自回归语言模型,构建“表征—解构—推理”全链条系统,实现从静态特征分析向时序病程推理的范式跃迁。项目创新包括:①结合预训练模型与知识库实现深度多模态表征; ②构建统一特征空间推动患者亚群识别与标志物发现;③开发高精度用药推荐模型; ④创新语言模型解析病程演变。预期成果包括再住院率降低30%、提升治疗响应率,推动精神疾病诊疗向可解释、精准、智能化转型,促进医疗AI在精神专科的落地应用。
EHR-based AI Modeling of Schizophrenia Heterogeneity and Multimodal Diagnostic Decision-Making
This project targets the clinical heterogeneity of schizophrenia by leveraging over 10,000 inpatient electronic medical records from Shanghai Mental Health Center. We propose a multimodal intelligent decision model integrating pretrained representations, self-supervised contrastive learning, and autoregressive language models. A full-stack “representation–deconstruction–reasoning” framework enables dynamic disease trajectory modeling beyond static analysis.Key innovations include: (1) deep multimodal embedding via pretrained models and knowledge bases; (2) unified feature space for patient subtyping and biomarker discovery; (3) accurate medication recommendation for prolonged hospitalization; and (4) autoregressive modeling of disease progression. The system aims to reduce rehospitalization by over 30% and establish an explainable, AI-powered paradigm for psychiatric decision support.


儿童青少年情绪问题分级的认知脑机制及生物标志:
本课题聚焦儿童青少年情绪问题的分级脑机制与生物标志物识别,假设脑多系统结构与功能发育的协调性,能更准确反映不同年龄和严重程度下情绪障碍的脑特征,进而影响认知功能。为识别潜在的外周分子标志物, 围绕关键科学问题1:不同分级情绪问题的认知、脑机制与生物标志,本课题将基于年龄与严重程度分级,基于多变量数据库,涵盖问卷、认知测量、ERP、MRI、遗传与代谢组数据。 研究将从以下两个方向展开: 认知—脑机制联动研究:系统分析情绪问题与知觉、注意、工作记忆等认知功能之间的关系, 揭示其在不同分级下的神经基础;多模态生物标志物智能发现:构建“生物-脑-认知-疾病”多模态图神经网络模型,基于自监督学习识别跨模态特征图谱,并结合迁移学习,发现区分伴/不伴自伤行为的严重情绪障碍的关键标志物和干预响应指标。
Study on the Cognitive and Neural Mechanisms and Biomarkers of Stratified Emotional Problems in Children and Adolescents
This project investigates the neural and biological basis of emotional problems in children and adolescents across different severity levels. We hypothesize that coordinated brain development reflects disease severity and cognitive impact. Using a multimodal database with behavioral, ERP, MRI, genetic, and metabolic data, we will explore two aims: Map the interaction between emotional symptoms and cognition; Use self-supervised graph learning to identify biomarkers linking biology, brain, and cognition, distinguishing cases with or without self-injury. Findings will support brain-targeted interventions and stratified, data-driven care.
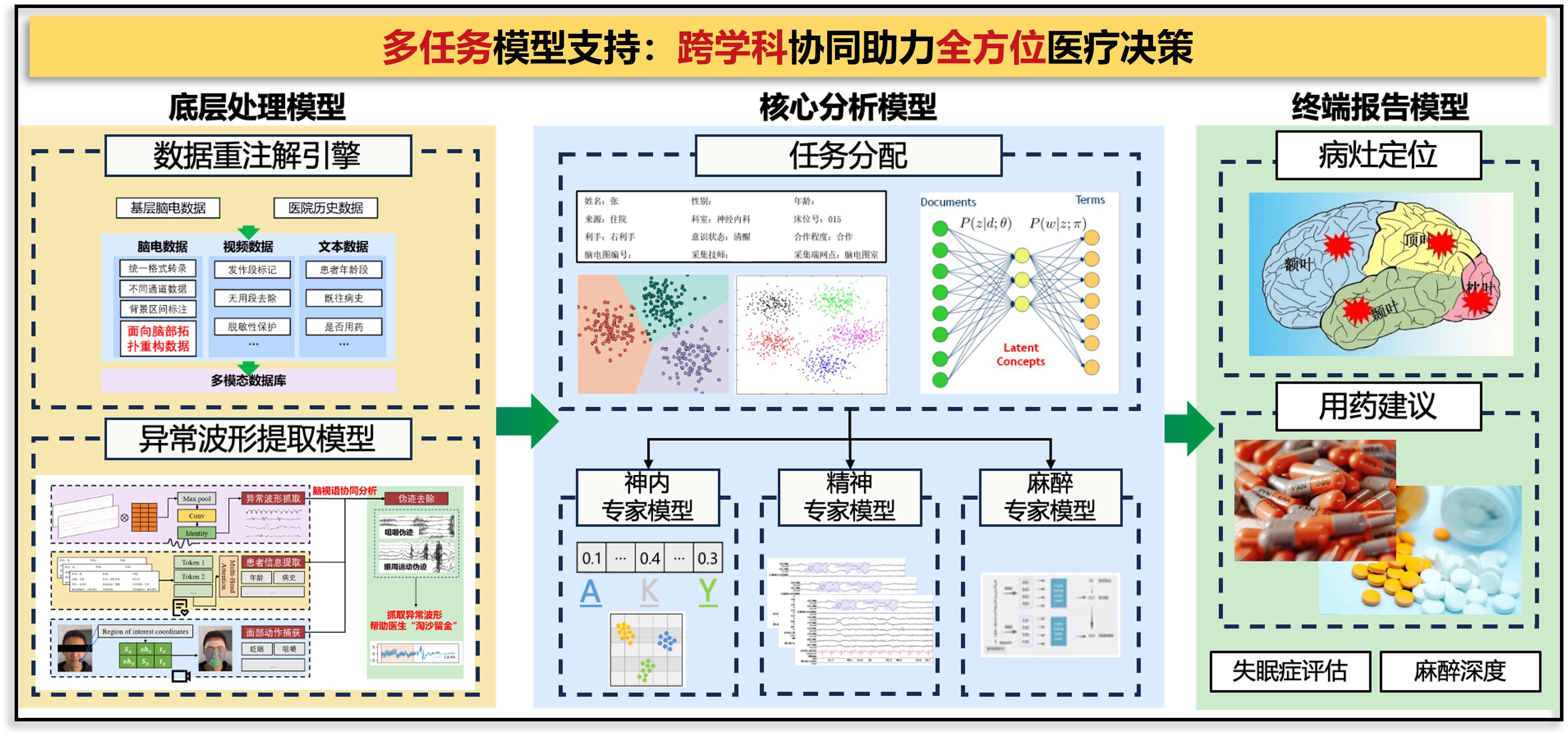
基于临床脑电数据的自动解析与智能诊疗辅助系统研究:
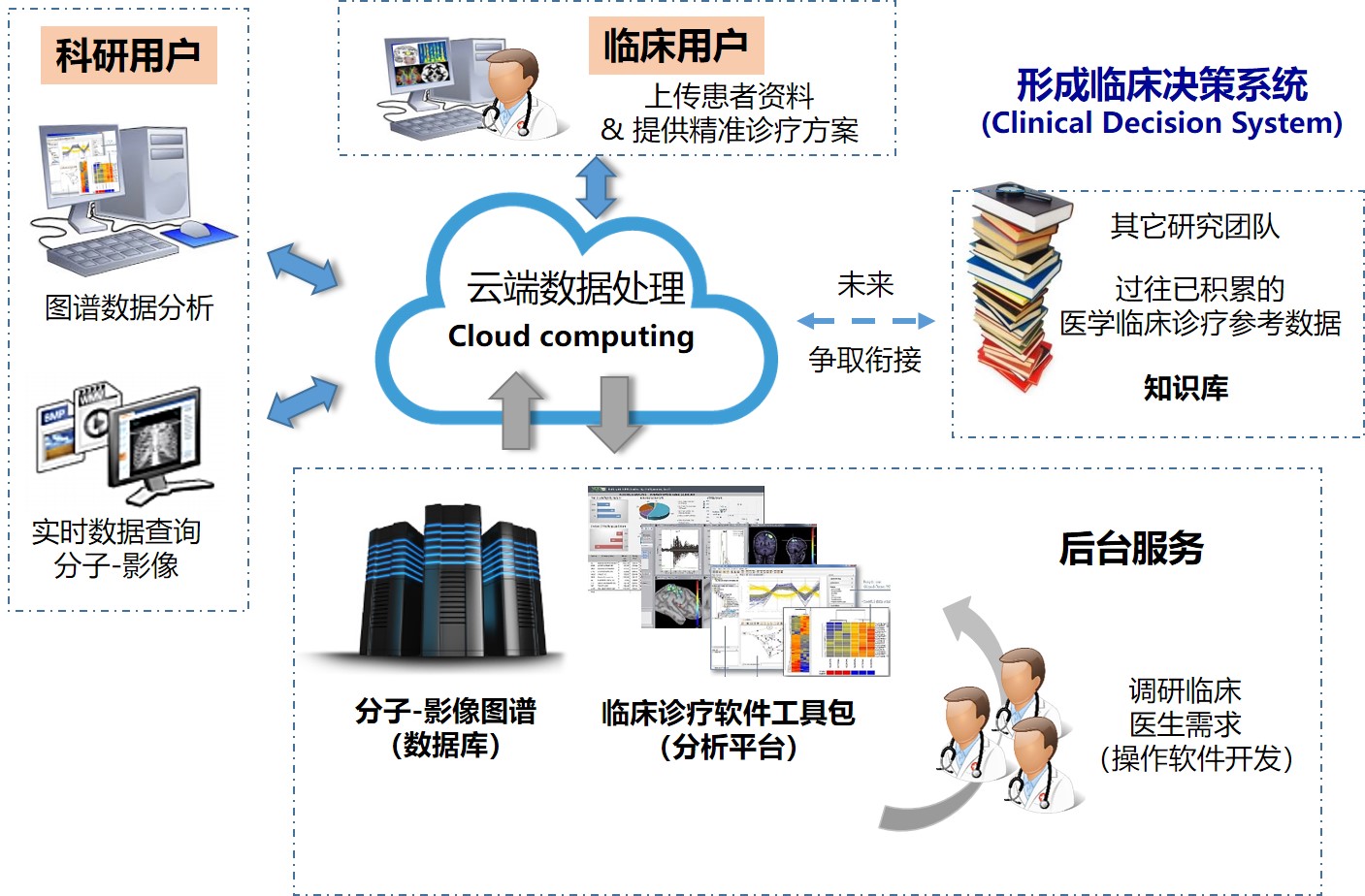
本项目致力于构建一个面向临床脑电图(EEG)数据的自动解析与智能辅助诊疗系统,针对传统脑电判读效率低、依赖专家经验、数据利用率有限等问题,提出融合多任务学习、自监督特征提取与多模态信息整合的解决方案。 系统由底层数据重注解引擎、异常波形识别模型、任务驱动的多专科分析模块以及终端报告生成模块构成,实现了从脑电异常自动识别、伪迹剔除,到病灶定位、用药建议、麻醉深度与睡眠评估的全过程智能化支持。 同时,结合时序建模与风险评分机制,开发癫痫发作的早期预警模型,为高风险患者提供前瞻性干预依据。 项目创新性地整合“生理信号+临床语义+任务导向”多维信息流,推动脑电AI在癫痫、失眠、麻醉等多个应用场景中的落地转化,为精准神经调控与个体化诊疗提供技术支撑。
Research on an Automated EEG Analysis and Intelligent Clinical Decision Support System Based on Clinical Data
This project develops an intelligent system for automated analysis of clinical EEG data, addressing limitations such as low efficiency, expert dependency, and poor data utilization. The system integrates multi-task learning, self-supervised feature extraction, and multimodal data fusion, and includes modules for data re-annotation, abnormal waveform detection, task-specific analysis, and automated report generation. It supports end-to-end functions from anomaly identification to lesion localization, medication advice, and sleep/anesthesia assessment. A seizure risk prediction model based on temporal features enables early warning for high-risk patients. The system promotes the application of EEG-based AI in epilepsy, insomnia, and anesthesia, supporting precision neuromodulation and personalized care..
基于足底压力的步态分析与帕金森病智能诊断研究:
本项目围绕人工智能在步态分析与神经疾病诊断中的应用,探索基于足底压力(GRF)数据的智能识别方法,旨在实现对帕金森病等运动障碍的高效、精准评估。通过引入AI驱动的建模策略, 系统能够从个体步态中提取关键信息,辅助疾病筛查、分级评估及功能状态判断。相较传统依赖人工特征和经验判断的方法,该系统具有更强的自动化处理能力和广泛的适应性,尤其在帕金森病的早期识别与动态监测中展现出显著优势。 项目预期推动步态数据在临床智能诊疗中的深度融合,为神经退行性疾病的个体化管理和远程健康监测提供创新路径。
AI-Enabled Gait Analysis and Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis Based on Plantar Pressure
This project focuses on the application of artificial intelligence in gait analysis and neurological disease diagnosis, exploring intelligent recognition methods based on ground reaction force (GRF) data. It aims to enable efficient and accurate assessment of movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. By leveraging AI-driven modeling strategies, the system can extract key information from individual gait patterns to support disease screening, severity grading, and functional evaluation. Compared to traditional approaches that rely on handcrafted features and expert interpretation, this system offers greater automation and adaptability, particularly excelling in the early detection and continuous monitoring of Parkinson’s disease. The project is expected to promote the integration of gait data into intelligent clinical decision-making, providing new solutions for personalized management and remote monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases.

其它科研项目还包括基因组学方面的数据挖掘(机器学习)的转化医学研究,我们不间断的和校内外合作者开拓新的合作项目。
Other areas of interest include machine learning in the context of genomics and translational genetics. We are constantly forming on and off-campus collaborations to further these and other areas of interest.